Read: Graph Quadratic Functions
Learning Objectives
- Graph a quadratic function using a table of values
- Identify important features of the graphs of a quadratic functions of the form [latex]f(x)=ax^2+bx+c[/latex]
| x | f(x) |
|---|---|
| [latex]−2[/latex] | [latex]4[/latex] |
| [latex]−1[/latex] | [latex]1[/latex] |
| [latex]0[/latex] | [latex]0[/latex] |
| [latex]1[/latex] | [latex]1[/latex] |
| [latex]2[/latex] | [latex]4[/latex] |
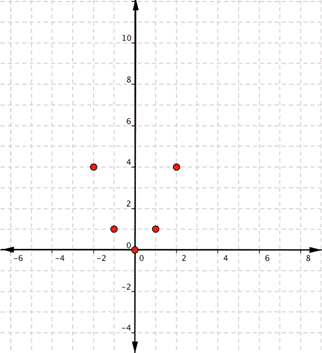 Since the points are not on a line, you can’t use a straight edge. Connect the points as best you can, using a smooth curve (not a series of straight lines). You may want to find and plot additional points (such as the ones in blue here). Placing arrows on the tips of the lines implies that they continue in that direction forever.
Since the points are not on a line, you can’t use a straight edge. Connect the points as best you can, using a smooth curve (not a series of straight lines). You may want to find and plot additional points (such as the ones in blue here). Placing arrows on the tips of the lines implies that they continue in that direction forever.
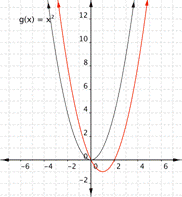
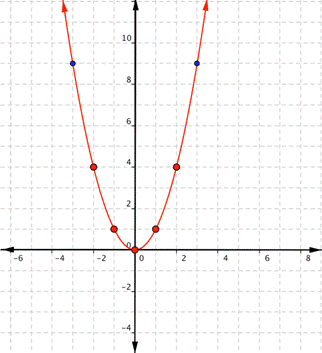 Notice that the shape is similar to the letter U. This is called a parabola. One-half of the parabola is a mirror image of the other half. The line that goes down the middle is called the line of reflection, in this case that line is they y-axis. The lowest point on this graph is called the vertex.
In the following video we show an example of plotting a quadratic function using a table of values.
https://youtu.be/wYfEzOJugS8
The equations for quadratic functions have the form [latex]f(x)=ax^{2}+bx+c[/latex] where [latex] a\ne 0[/latex]. In the basic graph above, [latex]a=1[/latex], [latex]b=0[/latex], and [latex]c=0[/latex].
Changing a changes the width of the parabola and whether it opens up ([latex]a>0[/latex]) or down ([latex]a<0[/latex]). If a is positive, the vertex is the lowest point, if a is negative, the vertex is the highest point. In the following example, we show how changing the value of a will affect the graph of the function.
Notice that the shape is similar to the letter U. This is called a parabola. One-half of the parabola is a mirror image of the other half. The line that goes down the middle is called the line of reflection, in this case that line is they y-axis. The lowest point on this graph is called the vertex.
In the following video we show an example of plotting a quadratic function using a table of values.
https://youtu.be/wYfEzOJugS8
The equations for quadratic functions have the form [latex]f(x)=ax^{2}+bx+c[/latex] where [latex] a\ne 0[/latex]. In the basic graph above, [latex]a=1[/latex], [latex]b=0[/latex], and [latex]c=0[/latex].
Changing a changes the width of the parabola and whether it opens up ([latex]a>0[/latex]) or down ([latex]a<0[/latex]). If a is positive, the vertex is the lowest point, if a is negative, the vertex is the highest point. In the following example, we show how changing the value of a will affect the graph of the function.
Example
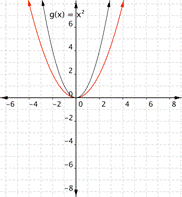
Match the following functions with their graph. a) [latex] \displaystyle f(x)=3{{x}^{2}}[/latex] b) [latex] \displaystyle f(x)=-3{{x}^{2}}[/latex] c) [latex] \displaystyle f(x)=\frac{1}{2}{{x}^{2}}[/latex] 1)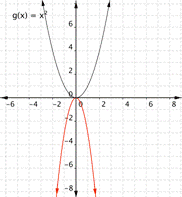 2)
2)
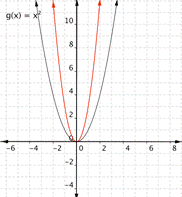 3)
3)
Answer:
Function a) [latex] \displaystyle f(x)=3{{x}^{2}}[/latex] means that inputs are squared and then multiplied by three, so the outputs will be greater than they would have been for [latex]f(x)=x^2[/latex]. This results in a parabola that has been squeezed, so graph [latex]2[/latex] is the best match for this function.
 Function b) [latex] \displaystyle f(x)=-3{{x}^{2}}[/latex] means that inputs are squared and then multiplied by negative three, so the outputs will be farther away from the [latex]x[/latex]-axis than they would have been for [latex]f(x)=x^2[/latex], but negative in value, so graph [latex]1[/latex] is the best match for this function.
Function b) [latex] \displaystyle f(x)=-3{{x}^{2}}[/latex] means that inputs are squared and then multiplied by negative three, so the outputs will be farther away from the [latex]x[/latex]-axis than they would have been for [latex]f(x)=x^2[/latex], but negative in value, so graph [latex]1[/latex] is the best match for this function.
 Function c) [latex] \displaystyle f(x)=\frac{1}{2}{{x}^{2}}[/latex] means that inputs are squared then multiplied by [latex]\dfrac{1}{2}[/latex], so the outputs are less than they would be for [latex]f(x)=x^2[/latex]. This results in a parabola that has been opened wider than[latex]f(x)=x^2[/latex]. Graph [latex]3[/latex] is the best match for this function.
Function c) [latex] \displaystyle f(x)=\frac{1}{2}{{x}^{2}}[/latex] means that inputs are squared then multiplied by [latex]\dfrac{1}{2}[/latex], so the outputs are less than they would be for [latex]f(x)=x^2[/latex]. This results in a parabola that has been opened wider than[latex]f(x)=x^2[/latex]. Graph [latex]3[/latex] is the best match for this function.

Answer
Function a) matches graph [latex]2[/latex] Function b) matches graph [latex]1[/latex] Function c) matches graph [latex]3[/latex]Example
Match the following functions with their graph. a) [latex] \displaystyle f(x)={{x}^{2}}+3[/latex] b) [latex] \displaystyle f(x)={{x}^{2}}-3[/latex] 1)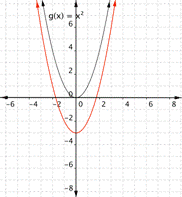 2)
2)
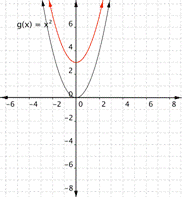
Answer:
Function a) [latex] \displaystyle f(x)={{x}^{2}}+3[/latex] means square the inputs then add three, so every output will be moved up [latex]3[/latex] units. The graph that matches this function best is [latex]2[/latex].
 Function b) [latex] \displaystyle f(x)={{x}^{2}}-3[/latex] means square the inputs then subtract three, so every output will be moved down [latex]3[/latex] units. The graph that matches this function best is [latex]1[/latex].
Function b) [latex] \displaystyle f(x)={{x}^{2}}-3[/latex] means square the inputs then subtract three, so every output will be moved down [latex]3[/latex] units. The graph that matches this function best is [latex]1[/latex].

Example
Match the following functions with their graph. a) [latex] \displaystyle f(x)={{x}^{2}}+2x[/latex] b) [latex] \displaystyle f(x)={{x}^{2}}-2x[/latex] a)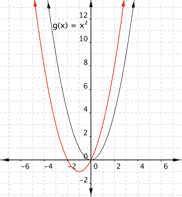 b)
b)
Answer:
Find the vertex of function a)[latex] \displaystyle f(x)={{x}^{2}}+2x[/latex].
[latex-display]a = 1, b = 2[/latex-display]
x-value:
[latex-display]\dfrac{-b}{2a}=\dfrac{-2}{2(1)}=-1[/latex-display]
y-value:
[latex]f(\dfrac{-b}{2a})=(-1)^2+2(-1)=1-2=-1[/latex].
Vertex = [latex](-1,-1)[/latex], which means the graph that best fits this function is a)
 Find the vertex of function b) [latex]f(x)={{x}^{2}}-2x[/latex].
[latex-display]a = 1, b = -2[/latex-display]
x-value:
[latex-display]\dfrac{-b}{2a}=\dfrac{2}{2(1)}=1[/latex-display]
y-value:
[latex]f(\dfrac{-b}{2a})=(1)^2-2(1)=1-2=-1[/latex].
Vertex = [latex](1,-1)[/latex], which means the graph that best fits this function is b)
Find the vertex of function b) [latex]f(x)={{x}^{2}}-2x[/latex].
[latex-display]a = 1, b = -2[/latex-display]
x-value:
[latex-display]\dfrac{-b}{2a}=\dfrac{2}{2(1)}=1[/latex-display]
y-value:
[latex]f(\dfrac{-b}{2a})=(1)^2-2(1)=1-2=-1[/latex].
Vertex = [latex](1,-1)[/latex], which means the graph that best fits this function is b)

Properties of a Parabola
For [latex] \displaystyle f(x)=a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c[/latex], where a, b, and c are real numbers.- The parabola opens upward if [latex]a > 0[/latex] and downward if [latex]a < 0[/latex].
- a changes the width of the parabola. The parabola gets narrower if [latex]|a|> 1[/latex] and wider if [latex]|a|<1[/latex].
- The vertex depends on the values of a, b, and c. The vertex is [latex]\left(\dfrac{-b}{2a},f\left( \dfrac{-b}{2a}\right)\right)[/latex].
Example
Graph [latex]f(x)=−2x^{2}+3x–3[/latex].Answer: Before making a table of values, look at the values of a and c to get a general idea of what the graph should look like. [latex]a=−2[/latex], so the graph will open down and be thinner than [latex]f(x)=x^{2}[/latex]. [latex]c=−3[/latex], so it will move to intercept the y-axis at [latex](0,−3)[/latex]. To find the vertex of the parabola, use the formula [latex] \displaystyle \left( \dfrac{-b}{2a},f\left( \dfrac{-b}{2a} \right) \right)[/latex]. Finding the vertex may make graphing the parabola easier.
[latex]\text{Vertex }\text{formula}=\left( \dfrac{-b}{2a},f\left( \dfrac{-b}{2a} \right) \right)[/latex]
x-coordinate of vertex:[latex] \displaystyle \dfrac{-b}{2a}=\dfrac{-(3)}{2(-2)}=\dfrac{-3}{-4}=\dfrac{3}{4}[/latex]
y-coordinate of vertex:[latex] \displaystyle \begin{array}{l}f\left( \dfrac{-b}{2a} \right)=f\left( \dfrac{3}{4} \right)\\\,\,\,f\left( \dfrac{3}{4} \right)=-2{{\left( \dfrac{3}{4} \right)}^{2}}+3\left( \dfrac{3}{4} \right)-3\\\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,=-2\left( \dfrac{9}{16} \right)+\dfrac{9}{4}-3\\\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,=\dfrac{-18}{16}+\dfrac{9}{4}-3\\\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,=\dfrac{-9}{8}+\dfrac{18}{8}-\dfrac{24}{8}\\\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,=-\dfrac{15}{8}\end{array}[/latex]
Vertex: [latex] \displaystyle \left( \dfrac{3}{4},-\dfrac{15}{8} \right)[/latex] Use the vertex, [latex] \displaystyle \left( \dfrac{3}{4},-\dfrac{15}{8} \right)[/latex], and the properties you described to get a general idea of the shape of the graph. You can create a table of values to verify your graph. Notice that in this table, the x values increase. The y values increase and then start to decrease again. That indicates a parabola.| x | f(x) |
|---|---|
| [latex]−2[/latex] | [latex]−17[/latex] |
| [latex]−1[/latex] | [latex]−8[/latex] |
| [latex]0[/latex] | [latex]−3[/latex] |
| [latex]1[/latex] | [latex]−2[/latex] |
| [latex]2[/latex] | [latex]−5[/latex] |
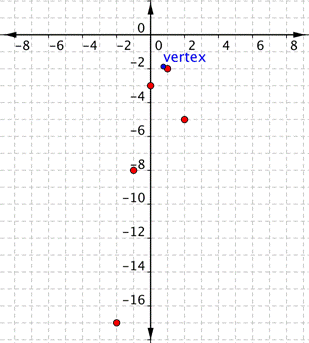
Answer
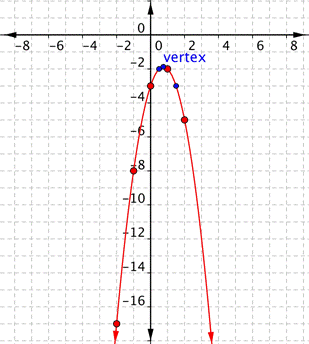 Connect the points as best you can, using a smooth curve. Remember that the parabola is two mirror images, so if your points don’t have pairs with the same value, you may want to include additional points (such as the ones in blue here). Plot points on either side of the vertex.
[latex]x=\Large\frac{1}{2}[/latex] and [latex]x=\Large\frac{3}{2}[/latex] are good values to include.
Connect the points as best you can, using a smooth curve. Remember that the parabola is two mirror images, so if your points don’t have pairs with the same value, you may want to include additional points (such as the ones in blue here). Plot points on either side of the vertex.
[latex]x=\Large\frac{1}{2}[/latex] and [latex]x=\Large\frac{3}{2}[/latex] are good values to include.
Licenses & Attributions
CC licensed content, Original
- Graph a Quadratic Function Using a Table of Value and the Vertex. Authored by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com) for Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution.
- Revision and Adaptation. Provided by: Lumen Learning License: CC BY: Attribution.
CC licensed content, Shared previously
- Unit 17: Functions, from Developmental Math: An Open Program. Provided by: Monterey Institute of Technology and Education Located at: https://www.nroc.org/. License: CC BY: Attribution.
- Ex: Graph a Quadratic Function Using a Table of Values. Authored by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com) for Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution.
