Solutions
Solutions to Try Its
1. The path passes through the origin and has vertex at [latex]\left(-4,\text{ }7\right)[/latex], so [latex]\left(h\right)x=-\frac{7}{16}{\left(x+4\right)}^{2}+7[/latex]. To make the shot, [latex]h\left(-7.5\right)[/latex] would need to be about 4 but [latex]h\left(-7.5\right)\approx 1.64[/latex]; he doesn’t make it. 2. [latex]g\left(x\right)={x}^{2}-6x+13[/latex] in general form; [latex]g\left(x\right)={\left(x - 3\right)}^{2}+4[/latex] in standard form 3. The domain is all real numbers. The range is [latex]f\left(x\right)\ge \frac{8}{11}[/latex], or [latex]\left[\frac{8}{11},\infty \right)[/latex]. 4. y-intercept at (0, 13), No x-intercepts 5. a. 3 seconds b. 256 feet c. 7 secondsSolutions to Odd-Numbered Exercises
1. When written in that form, the vertex can be easily identified. 3. If [latex]a=0[/latex] then the function becomes a linear function. 5. If possible, we can use factoring. Otherwise, we can use the quadratic formula. 7. [latex]f\left(x\right)={\left(x+1\right)}^{2}-2[/latex], Vertex [latex]\left(-1,-4\right)[/latex] 9. [latex]f\left(x\right)={\left(x+\frac{5}{2}\right)}^{2}-\frac{33}{4}[/latex], Vertex [latex]\left(-\frac{5}{2},-\frac{33}{4}\right)[/latex] 11. [latex]f\left(x\right)=3{\left(x - 1\right)}^{2}-12[/latex], Vertex [latex]\left(1,-12\right)[/latex] 13. [latex]f\left(x\right)=3{\left(x-\frac{5}{6}\right)}^{2}-\frac{37}{12}[/latex], Vertex [latex]\left(\frac{5}{6},-\frac{37}{12}\right)[/latex] 15. Minimum is [latex]-\frac{17}{2}[/latex] and occurs at [latex]\frac{5}{2}[/latex]. Axis of symmetry is [latex]x=\frac{5}{2}[/latex]. 17. Minimum is [latex]-\frac{17}{16}[/latex] and occurs at [latex]-\frac{1}{8}[/latex]. Axis of symmetry is [latex]x=-\frac{1}{8}[/latex]. 19. Minimum is [latex]-\frac{7}{2}[/latex] and occurs at –3. Axis of symmetry is [latex]x=-3[/latex]. 21. Domain is [latex]\left(-\infty ,\infty \right)[/latex]. Range is [latex]\left[2,\infty \right)[/latex]. 23. Domain is [latex]\left(-\infty ,\infty \right)[/latex]. Range is [latex]\left[-5,\infty \right)[/latex]. 25. Domain is [latex]\left(-\infty ,\infty \right)[/latex]. Range is [latex]\left[-12,\infty \right)[/latex]. 27. [latex]\left\{2i\sqrt{2},-2i\sqrt{2}\right\}[/latex] 29. [latex]\left\{3i\sqrt{3},-3i\sqrt{3}\right\}[/latex] 31. [latex]\left\{2+i,2-i\right\}[/latex] 33. [latex]\left\{2+3i,2 - 3i\right\}[/latex] 35. [latex]\left\{5+i,5-i\right\}[/latex] 37. [latex]\left\{2+2\sqrt{6}, 2 - 2\sqrt{6}\right\}[/latex] 39. [latex]\left\{-\frac{1}{2}+\frac{3}{2}i, -\frac{1}{2}-\frac{3}{2}i\right\}[/latex] 41. [latex]\left\{-\frac{3}{5}+\frac{1}{5}i, -\frac{3}{5}-\frac{1}{5}i\right\}[/latex] 43. [latex]\left\{-\frac{1}{2}+\frac{1}{2}i\sqrt{7}, -\frac{1}{2}-\frac{1}{2}i\sqrt{7}\right\}[/latex] 45. [latex]f\left(x\right)={x}^{2}-4x+4[/latex] 47. [latex]f\left(x\right)={x}^{2}+1[/latex] 49. [latex]f\left(x\right)=\frac{6}{49}{x}^{2}+\frac{60}{49}x+\frac{297}{49}[/latex] 51. [latex]f\left(x\right)=-{x}^{2}+1[/latex] 53. Vertex [latex]\left(1,\text{ }-1\right)[/latex], Axis of symmetry is [latex]x=1[/latex]. Intercepts are [latex]\left(0,0\right), \left(2,0\right)[/latex].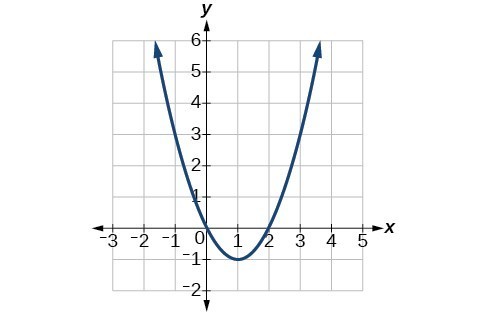 55. Vertex [latex]\left(\frac{5}{2},\frac{-49}{4}\right)[/latex], Axis of symmetry is [latex]\left(0,-6\right),\left(-1,0\right),\left(6,0\right)[/latex].
55. Vertex [latex]\left(\frac{5}{2},\frac{-49}{4}\right)[/latex], Axis of symmetry is [latex]\left(0,-6\right),\left(-1,0\right),\left(6,0\right)[/latex].
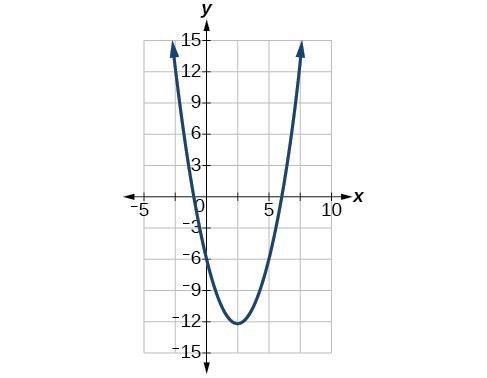 57. Vertex [latex]\left(\frac{5}{4}, -\frac{39}{8}\right)[/latex], Axis of symmetry is [latex]x=\frac{5}{4}[/latex]. Intercepts are [latex]\left(0, -8\right)[/latex].
57. Vertex [latex]\left(\frac{5}{4}, -\frac{39}{8}\right)[/latex], Axis of symmetry is [latex]x=\frac{5}{4}[/latex]. Intercepts are [latex]\left(0, -8\right)[/latex].
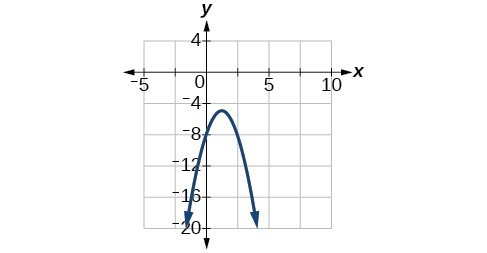 59. [latex]f\left(x\right)={x}^{2}-4x+1[/latex]
61. [latex]f\left(x\right)=-2{x}^{2}+8x - 1[/latex]
63. [latex]f\left(x\right)=\frac{1}{2}{x}^{2}-3x+\frac{7}{2}[/latex]
65. [latex]f\left(x\right)={x}^{2}+1[/latex]
67. [latex]f\left(x\right)=2-{x}^{2}[/latex]
69. [latex]f\left(x\right)=2{x}^{2}[/latex]
71. The graph is shifted up or down (a vertical shift).
73. 50 feet
75. Domain is [latex]\left(-\infty ,\infty \right)[/latex]. Range is [latex]\left[-2,\infty \right)[/latex].
77. Domain is [latex]\left(-\infty ,\infty \right)[/latex] Range is [latex]\left(-\infty ,11\right][/latex].
79. [latex]f\left(x\right)=2{x}^{2}-1[/latex]
81. [latex]f\left(x\right)=3{x}^{2}-9[/latex]
83. [latex]f\left(x\right)=5{x}^{2}-77[/latex]
85. 50 feet by 50 feet. Maximize [latex]f\left(x\right)=-{x}^{2}+100x[/latex].
87. 125 feet by 62.5 feet. Maximize [latex]f\left(x\right)=-2{x}^{2}+250x[/latex].
89. 6 and –6; product is –36; maximize [latex]f\left(x\right)={x}^{2}+12x[/latex].
91. 2909.56 meters
93. $10.70
59. [latex]f\left(x\right)={x}^{2}-4x+1[/latex]
61. [latex]f\left(x\right)=-2{x}^{2}+8x - 1[/latex]
63. [latex]f\left(x\right)=\frac{1}{2}{x}^{2}-3x+\frac{7}{2}[/latex]
65. [latex]f\left(x\right)={x}^{2}+1[/latex]
67. [latex]f\left(x\right)=2-{x}^{2}[/latex]
69. [latex]f\left(x\right)=2{x}^{2}[/latex]
71. The graph is shifted up or down (a vertical shift).
73. 50 feet
75. Domain is [latex]\left(-\infty ,\infty \right)[/latex]. Range is [latex]\left[-2,\infty \right)[/latex].
77. Domain is [latex]\left(-\infty ,\infty \right)[/latex] Range is [latex]\left(-\infty ,11\right][/latex].
79. [latex]f\left(x\right)=2{x}^{2}-1[/latex]
81. [latex]f\left(x\right)=3{x}^{2}-9[/latex]
83. [latex]f\left(x\right)=5{x}^{2}-77[/latex]
85. 50 feet by 50 feet. Maximize [latex]f\left(x\right)=-{x}^{2}+100x[/latex].
87. 125 feet by 62.5 feet. Maximize [latex]f\left(x\right)=-2{x}^{2}+250x[/latex].
89. 6 and –6; product is –36; maximize [latex]f\left(x\right)={x}^{2}+12x[/latex].
91. 2909.56 meters
93. $10.70Licenses & Attributions
CC licensed content, Shared previously
- Precalculus. Provided by: OpenStax Authored by: Jay Abramson, et al.. Located at: https://openstax.org/books/precalculus/pages/1-introduction-to-functions. License: CC BY: Attribution. License terms: Download For Free at : http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected]..
